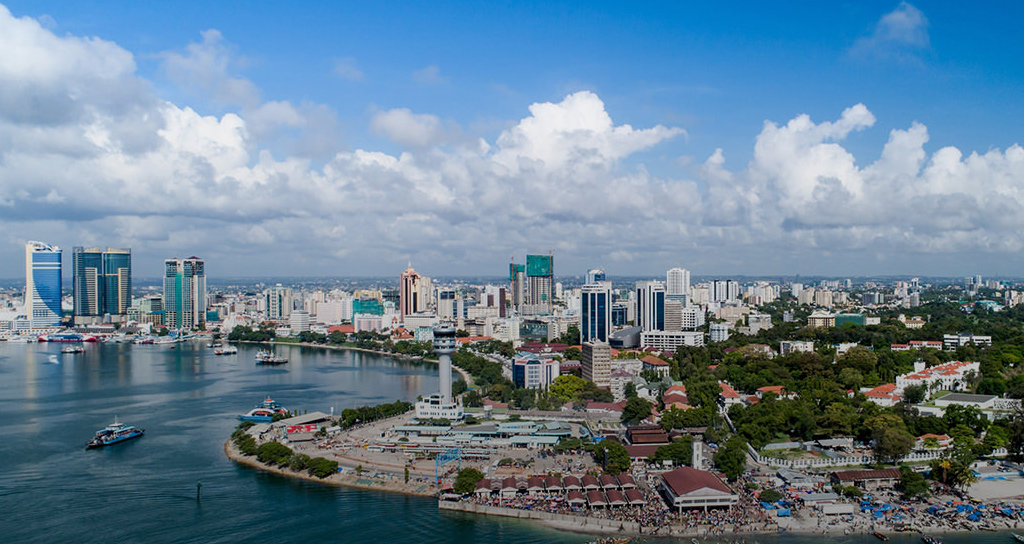
Investment Opportunities In Tanzania
The country gears up to become an industrialized middle-income country by 2025. In line with this vision we have decided to put greater accent on building a strong industrial base. To this end, Tanzania has set up Export Processing Zones (EPZs) and Special Economic Zones (SEZs) as ponds of industrial growth and services to promote export trade. The EPZ scheme promotes investment in manufacturing sector mainly for export while SEZ scheme involves other sectors such as agriculture, trade, tourism, mining, and forestry.
Tanzania offers generous fiscal incentives under the Export Processing Zone/Special Economic Zone (EPZ/SEZ) schemes to attract Foreign Direct Investments (FDIs) and Domestic Direct Investments (DDIs).
Improving the transportation infrastructure is a key priority for the Government of Tanzania. Developing the nation’s roads, ports, railways and airport infrastructure is critical for the country to improve its internal and external trade and commercial activities. The sector’s further development includes improvements in the energy sector as Tanzania strives to become a middle-income country.
Infrastructure projects provide exciting opportunities for investors looking to capitalize on Tanzania’s fast-growing economy.
Investment Opportunities
Tanzania offers abundant natural resources which provide for plenty of raw materials for the manufacturing industries such as cotton for garment and textile industries, sisal for canvassing, iron for steel, as well as various minerals and gemstones. Opportunities exist for establishment of SEZs/EPZs.
Under Manufacturing sector, Tanzania offers Opportunities for
- Establishment of SEZs/EPZs, Industrial parks and logistics centres,
- Etablishing motor vehicle and motorcycle assembly plants and spare parts production facilities for domestic and regional markets,
- Construction of a liquefied natural gas (LNG) plant and Construction, rehabilitation and providing requisite support to strategic pharmaceutical industries,
- Production of construction materials such as ceramics and cement,
- Development of iron and steel industries,
- Agro-industries and agro-processing to add value to agricultural, livestock, forestry and fisheries products.
- Sugar industry (considering a demand gap currently met through imports).
- Increasing domestic edible oil production (there is a need to reduce dependence on imports).
- Food and beverages manufacturing has a lot of potential and includes manufacturing, processing, and preservation of meat, fish, fruit, vegetables, oils and fats;
- Manufacture of dairy products; manufacture of grain mill products, starches and starch products and prepared animal feeds;
- Manufacture of other food products (e.g. bread, sugar, chocolate, pasta, coffee, nuts and spices)
- The manufacture of bottled and canned soft drinks, fruit juices, beer, and wines.
- Tanzania is fully reliant on imported automotive products such as passenger cars
- Tanzania has made discoveries of natural gas, soda ash, and other minerals required for petrol, gas, and chemical industries
- Tanzania has a sugar demand gap of about 220,000 tons met through imports
- In 2015 Tanzania imported 60% of its edible oil
- Tanzania is identified as one of the 20 countries that will in the near future offer the most opportunities for consumer goods companies globally, particularly for food and beverages
There are enormous opportunities in the services sector particularly ICT which is among the fastest-growing sub-sectors in Tanzania. There has been a rapid growth and transformation of the communications market in Tanzania in the last 10 years. The ICT market has grown in terms of subscribers, variety of services and the expansion of the coverage area.
Tanzania has a total surface area of 945,037 sq. km. The area of freshwater cover is estimated at 54,337 sq. km., which is about 6.1 percent of the total country’s surface area. The country has a Territorial Sea of 64,000 sq. km., an Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) covering an area of about 223,000 sq. km. and a stretch of a coastline of about 1,424 km long all in the Indian Ocean, and other inland water bodies (major and minor lakes, rivers, dams, ponds and wetlands), covering about 5,000 sq. km. The country shares three major inland lakes: Lake Victoria (shared with Kenya and Uganda), Lake Tanganyika (shared with Burundi, DRC and Zambia) and Lake Nyasa (shared with Malawi and Mozambique).
- Establishment of fishing port and fishing in the Exclusive Economic Zone,
- Establishing fish processing plants and modern fishing boat building yards.
- Establishment of dry docking and eco-tourism facilities.
- Around 3000 hectares suitable for shrimp farming in Mafia Island.
- Establishment of commercial fish cage culture in both marine and freshwater areas
- Cultured species including: Mud crabs, Oysters, Grouper and Scallops for mariculture
- Fresh water species including : Tilapias, African Catfish , Rainbow Trout and Freshwater prawns
- Production of formulated fish feeds and live fish food(eg. Earthworms)
- deep sea fishing, fish processing,
- Value addition in fish and other fisheries products, cold chain, , manufacturing of fishing gear and accessories.
- Other areas include prawn/shrimp farming, mud-crab farming, pearl culture, seaweed farming, hatchery for fingerlings production,
- Fishing and culture of ornamental fish, fish feeds production and live fish food production.
- Tanzania is one of the largest fishing nations in Africa, according to FAO; it is ranked in the top 10 countries in terms of total capture fisheries production.
- The annual fish production is about 341,065 tons. In addition, the sector contributed about 1.4 percent to the GDP (National Statistics Bureau; 2010) and 10 percent to the national foreign exchange earnings.
- The sector employs more than 177,527 full time fishermen and about other 4 million people earn their livelihoods from the fisheries sector (Fisheries Statistics, 2011).
- For the years 2005 – 2010, fish and fishery products exports from Tanzania earned the country US$ 195.2 million per annum.
- The country shares three major inland lakes: Lake Victoria (shared with Kenya and Uganda), Lake Tanganyika (shared with Burundi, DRC and Zambia) and Lake Nyasa (shared with Malawi and Mozambique).
Tanzania has outstanding natural resources for livestock development including resilient livestock breeds, extensive rangelands and diverse natural vegetation of 88.6 million hectares of land resources in the country, 60 million hectares are deemed suitable for grazing.
- Establishment of joint venture projects with National Ranching Company (NARCO) and other privately owned ranches to modernize the existing ranches,
- establishment of new ranches (cattle, sheep and goats) and farms (poultry and piggery),
- livestock fattening,
- Establishment of modern slaughtering facilities and processing plants,
- Establishment of breeders farms for grand and parent stock,
- Establishment of animal feeds processing plants to supply feeds to the large local small and medium scale producers,
- Establishment of commercial layers and broiler farms and
- Establishment of broiler processing plants and act as hub/market for small and medium scale poultry production.
- Establishment of tanneries, production of footwear and leather goods,
- Establishment of dairy farms and facilities for milk processing.
- Investment in Livestock farming focusing on Beef, Dairy, Chicken, Hides and Skins as prioritized products.
- By the year 2015 Tanzania had the third largest livestock population on the African continent comprising 25 million cattle, 98% of which were indigenous breeds, complemented by 16.7 million goats, 8 million sheep, 2.4 million pigs, and 36 million chickens.
- All foundational economic indicators point to dramatic increase in national, regional and global demand for Tanzanian livestock products as populations grow in number and affluence. With demand for meat in Tanzania expected to triple by 2030.
- Tanzanian with its geography linking east and southern Africa and interior nations to the coast is well placed to be a major player in regional livestock market investments.
- Trade in meat has increased significantly, with more and more countries seeking to close their supply gap through imports. Major meat exporters, especially in South America, face logistical challenges to supply new growth areas in Africa, Middle East and Asia.
Tanzania’s tourism industry accounts for about 24.0 % of its exports and 17.2% of GDP.This is a fast-growing sector that offers plenty of investment opportunities.
Tourism is a fast-growing sector that offers plenty of investment opportunities for investing in areas such as
- Construction of Tourist Hotels in towns, game parks as well as along the 850 miles coast line of mainland Tanzania and the beautiful shores of the spice Island of Zanzibar
- Establishment of leisure parks.
- Construction of golf courses.
- Investing in conference tourism facilities.
- Provision of air/ground transport.
- Tour operations and trophy hunting.
- Sea and lake cruising.
- Development of eco-tourism facilities.
- Beach tourism, cultural and historical sites
- Tanzania is the only country in the world that has allocated more than 25 percent of its total area for wildlife and other resources’ conservation.
- There are 16 National Parks, 28 Game Reserves, 44 Game Controlled areas, 1 Conservation area and 2 Marine Parks.
- Tanzania wildlife resources are considered among the finest in the world and have been widely known for many years.
- The industry continued to grow in 2014 as exhibited by increase in the number of international tourist arrivals to 1,140,156 from 782,699 recorded in 2010. As a result, tourism earning increased to USD 2,006.32 million from USD 1,254.50 in 2010
.
Tanzania is endowed with diverse energy sources including biomass, natural gas, hydro, coal, geothermal, solar and wind power and uranium, much of which is untapped. Commercial energy sources i.e., petroleum and electricity, account for about 8% and 1.2%, respectively, of the primary energy used. Coal, solar and wind account for less than 1%.
- Generation, transportation and distribution of energy from various sources
- Power infrastructure development, rehabilitation and expansion
- Extraction of biofuels – Ethanol from sugar; Biodiesel from palm oil and jatropha
- Construction of Petroleum pipeline and Petroleum products offloading terminals development of upcountry storage and distribution facilities
- Geothermal exploration and development
- Rural Electrification
- Development of new and renewable energy resources, and
- Promotion of energy efficiency and conservation initiatives
- At present, 21% of the population with about 7.4 percent in the rural areas has access to electricity.
- The Tanzania power sector is dominated by a single vertically integrated national utility, Tanzania Electricity Supply Company Ltd (TANESCO).
- The total grid installed generation capacity of both TANESCO’s power plants and private producers is currently at 1,438.24 MW
- 561 MW is generated from TANESCO owned hydro power stations and thermal 658 MW
- National electricity connectivity is about 14%
- The contribution of non-hydro renewable energy for power generation is less than 5%
- Wood-fuel accounts for up to 90% of total national energy consumption, with about 2% from electricity and 8% from petroleum products.
.
Accommodation in Dar es Salaam and other cosmopolitan areas is in acute shortage due to, among other reasons, the rapid growth of economic projects, which have attracted a huge population of persons (international and local) with the need of residence. Investors may form a synergy with National Housing Corporation (NHC) or Tanzania Building Agency (TBA), or other private firms and provide commercial building solutions for residential and commercial purposes.
- Development and management of housing estates
- Erection and management of residential apartments
- Development and management of office buildings
- Building and management of conference and banquet facilities
- Creation and management of shopping malls
- Setting up and managing movie theatres and entertainment facilities
- Development and management of hotels
- Establishment and management of mixed use real estate properties
- Provision of home financing, etc.
- It is projected that half of Tanzania’s 45 million population will have moved to urban centres in the next 20 years, more has to be done in terms of offering more housing loans and constructing homes to meet the ever-growing housing needs
.
There have been several gas discoveries on the coastal shore of the Indian Ocean at Songosongo, Mnazi bay and Mkuranga in Coast Region. These discoveries are catalysts of natural gas developments in Tanzania. Currently there are 22 Oil Companies undertaking exploration activities for oil and gas in the country. These companies include: BG Group, Statoil, Petrobas and Ophir Energy. Tanzania is becoming a regional hub after flurry of discoveries, it is said to be blessed with over 41.7 trillion cubic feet of gas reserves at the latest estimates.
- Domestic Production and Marketing of Liquefied Natural Gas (LPG).
- Domestic Manufacturing of LPG cylinders, valves and regulators, installation of filling plants, retail distribution and development of simple, flexible and less expensive gas burners to encourage the use of gas instead of wood.
- Establishment of processing plants and industries for the production of; refined mineral oil, petroleum jelly and grease, fertilizers ; bituminous based water / damp proof building materials e.g. roofing sheets, floor tiles and tarpaulin
- Establishment of chemical industries e.g. distillation units for the production of Naphtha and other special boiling point solvents used in food processing.
- Development of petrochemicals industries.
- Establishment of LNG Projects.
- Small-scale production of chemicals and solvents e.g. chlorinated methane, Formaldehyde, Acetylene etc. from natural gas.
- Crude oil refining with efficient export facilities.
- There are still numerous deep-sea blocks that are yet to be explored at which Tanzania Petroleum Development Corporation (TPDC is inviting oil and gas companies and other specialized investors to participate in the exploration of hydrocarbons in Tanzania.
- Companies may apply for tendered out blocks for available blocks, successful companies will be invited to negotiate a Production Sharing Agreement (PSA)
- Currently, an open acreage includes: i. Deep offshore sedimentary basin comprising of 7 blocks, each with average size of 3,000 sq. km, that are located between 2,000 meters to 3,000 meters of water depths from 20° 30’E to 41°40’E and 7°30’ to 9°00S
- ii. North lake Tanganyika block located offshore on the western arm of the East African Rift System. The Deep offshore blocks have a good coverage of modern regional 2D seismic data, which can be viewed at the ION GX Technology of Huston, Texas and Western Geco of UK.
.
The banking sector in Tanzania has been booming, growing in assets and in profits Because of this, new merchant banks, commercial banks, bureau de change, insurance companies, a stock exchange and related financial units, have entered the market. There are four categories of banks, oriented towards different markets and clientele operating in Tanzania: local private banks, regional banks, international banks and multinational banks.
- Establishment of fully fledged Commercial Banks.
- Establishment of Development Financial Institution
- Establishment of Community Banks
- Establishment of Microfinance Banks
- Establishment of Financial Leasing Companies.
- The banking system in Tanzania (which dominates the financial system) is liquid and resilient to most of the shocks. Despite some indications of progress resulting from the reforms, the system falls short of what is needed to support economic growth. This results in high interest rates on loans, currently 12% to 20%, while the interest rates on deposits are at 2%.
.
F
The Communication Act of 1993 paved the way for advancement of the telecommunication sector, while the National Telecommunication Policy (NTP) of 1997 provided the framework for further reforms and private-sector engagement in the sector. A milestone in telecom sector was achieved by the establishment of the Tanzania Communications Regulatory Authority (TCRA) in 2003, as an independent agency for the regulating and licensing of postal, broadcast, and communication, industries. The TCRA is mandated to promote competition and economic efficiency, protect consumer interests, grant licenses and enforce license conditions, regulate tariffs, and monitor performance. Please refer to the next exhibit regarding subscribers of voice telecommunication in Tanzania.
- Provision and operation of Private Network Links employing cables, radio communications, or satellite, within Tanzania.
- Provision and operation of Public Mobile Communications (Cellular Mobile telephony, Paging, and Trunked Radio)
- Provision and operation of Community Telecommunication (Rural and Urban)
- Provision and operation of Value Added Network/Data Services (Internet, Voice Mail, Electronic Mail services)
- Sales and installation of Terminal Equipment.
- Repair and maintenance of telecommunications facilities, and
- Cabling (e.g. Telephone-external and internal wiring for residential, office etc.).
- Communication activities continue to grow at a rate of 20% annually due to increase in mobile phone activities.
- Tanzania is now connected to the fiber optic cable to global networks through India and Europe. This development has resulted in increased investments by internet service providers (ISP).
- The number of internet users was 4.9 million (2010 estimates), which implied that only 20% percent of people in Tanzania had access to internet services
- During the same year 2010, the tele-density of telecommunication sector grew by 50% percent.
- The TCRA has also approved a Converged Licensing Framework (CLF), which allows operators to offer any type of services with the technology of their choice with one single license. The licenses are technology-neutral and service-neutral.
- Following such convergence in licensing, Tanzania’s telecommunication sector has become more appealing to both Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and domestic capital, and is becoming one of the country’s fastest growing sectors
- Telecommunication market potential indicated positive signs, such as penetration rate of 61% percent; 24,345,279,292 minutes of national traffic; 201,827,164 minutes of traffic to international; and 253,811,569 minutes of traffic from international.
.
Broadcasting sector constitutes few players who own multiple TV stations and or radio channels. IPP Media, for instance, owns three TV channels, namely ITV, EATV, and Capital. Africa Media Group owns four TV channels, known as DTV, Channel 10, CTN and C2C, whereas Tanzania Broadcasting Corporation owns two TV channels, TBC1 and TBC2.
- Establishment of television production companies.
- Creating mainstream television programs for international market
- Provision of local content television channels for local market
- Management of the programs data stream
- Service of program guide .
- Channel capacity and reconfiguration management
- Transmission path redundancy and fail-safe systems
- News systems [for gathering and processing news]
- Digital audio equipment (for production and processing)
- Archiving (for the storage of audio and text)
- Automation (for scheduling and control), etc.
- TCRA data indicated that, there are now 29 television stations and 47 radio stations nationwide. .
- FM radio stations dominate the airwaves, most of them focusing on musical entertainment.
- December 2012, TCRA managed to perform a digital broadcast switch, which entails the end of analogue broadcast as most broadcasting is now digital